Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic medication, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain.
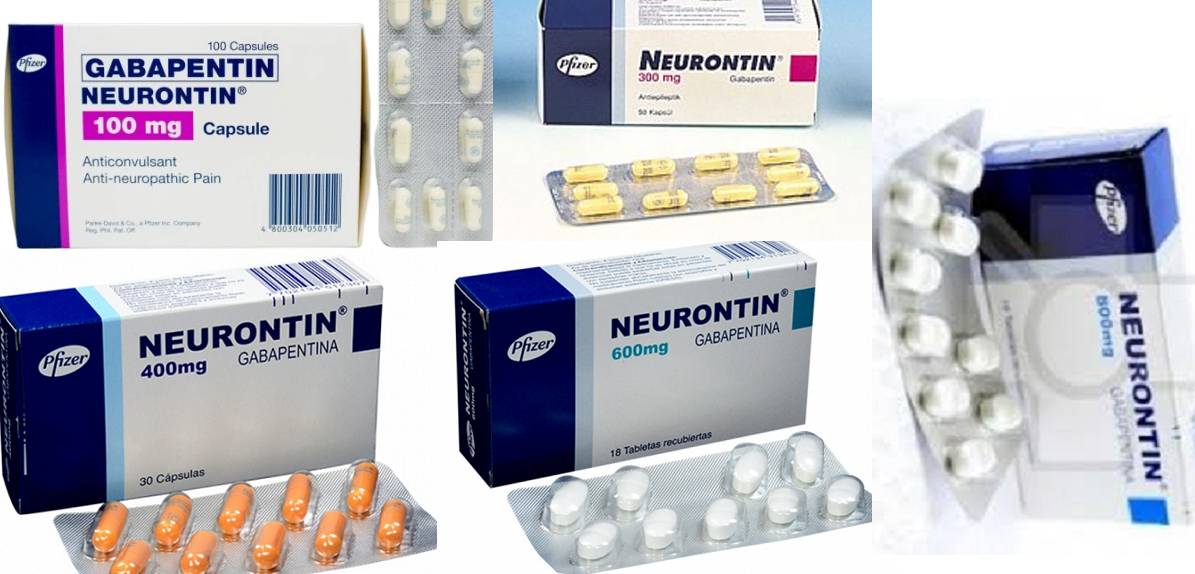
Gabapentin is used in adults to treat nerve pain caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster).
The Horizant brand of gabapentin is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS).
The Neurontin brand of gabapentin is also used to treatseizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old.
NEURONTIN is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing ofshingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults.
- Partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older with seizures.
How should this medicine be used?
Gabapentin comes as a capsule, a tablet, an extended-release (long-acting) tablet, and an oral solution (liquid) to take by mouth. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are usually taken with a full glass of water (8 ounces [240 milliliters]), with or without food, three times a day.
These medications should be taken at evenly spaced times throughout the day and night; no more than 12 hours should pass between doses. The extended-release tablet (Horizant) is taken with food once daily at about 5 PM. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take gabapentin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Gabapentin extended-release tablets cannot be substituted for another type of gabapentin product. Be sure that you receive only the type of gabapentin that was prescribed by your doctor. Ask your pharmacist if you have any questions about the type of gabapentin you were given.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole; do not cut, chew, or crush them.
If your doctor tells you to take one-half of a regular tablet as part of your dose, carefully split the tablet along the score mark. Use the other half-tablet as part of your next dose. Properly dispose of any half-tablets that you have not used within several days of breaking them.
If you are taking gabapentin to control seizures or PHN, your doctor will probably start you on a low dose of gabapentin and gradually increase your dose as needed to treat your condition. If you are taking gabapentin to treat PHN, tell your doctor if your symptoms do not improve during your treatment.
Gabapentin may help to control your condition but will not cure it. Continue to take gabapentin even if you feel well. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor, even if you experience side effects such as unusual changes in behavior or mood. If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. If you are taking gabapentin to treat seizures and you suddenly stop taking the medication, you may experience seizures more often. Your doctor may decrease your dose gradually over at least a week.
Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with gabapentin and each time you refill your prescription. Read the information carefully and ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also visit the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website (http://www.fda.gov/Drugs) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Guide.
Other uses for this medicine
Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes), and to treat and prevent hot flashes (sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating) in women who are being treated for breast cancer or who have experienced menopause (”change of life”, the end of monthly menstrual periods). Talk to your doctor about the risks of using this medication for your condition.
This medication may be prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special precautions should I follow?
Before taking gabapentin,
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to gabapentin, any other medications, or any of the inactive ingredients in the type of gabapentin you plan to take. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the inactive ingredients.
- you should know that gabapentin is available in different forms that may be prescribed for different uses. Ask your doctor to be sure that you are not taking more than one product that contains gabapentin.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: hydrocodone (in Hydrocet, in Vicodin, others), medications that make you feel dizzy or drowsy, morphine (Avinza, Kadian, MSIR, others), and naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprosyn, others). Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- if you are taking antacids such as Maalox or Mylanta, take them at least 2 hours before you take gabapentin tablets, capsules, or solution.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had kidney disease. If you will be taking the extended-release tablets, also tell your doctor if you need to sleep during the day and stay awake at night.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking gabapentin, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking gabapentin.
- you should know that this medication may make you drowsy or dizzy, may slow your thinking, and may cause loss of coordination. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how this medication affects you, and your doctor agrees that it is safe for you to begin these activities.
- if you are giving gabapentin to your child, you should know that your child’s behavior and mental abilities may change while he or she is taking gabapentin. Your child may have sudden changes in mood, become hostile or hyperactive, have difficulty concentrating or paying attention, or be drowsy or clumsy. Have your child avoid activities that could be dangerous, such as riding a bicycle, until you know how gabapentin affects him or her.
- remember that alcohol can add to the drowsiness caused by this medication.
- you should know that your mental health may change in unexpected ways and you may become suicidal (thinking about harming or killing yourself or planning or trying to do so) while you are taking gabapentin for the treatment of epilepsy, mental illness, or other conditions. A small number of adults and children 5 years of age and older (about 1 in 500 people) who took anticonvulsants such as gabapentin to treat various conditions during clinical studies became suicidal during their treatment. Some of these people developed suicidal thoughts and behavior as early as one week after they started taking the medication. There is a risk that you may experience changes in your mental health if you take an anticonvulsant medication such as gabapentin, but there may also be a risk that you will experience changes in your mental health if your condition is not treated. You and your doctor will decide whether the risks of taking an anticonvulsant medication are greater than the risks of not taking the medication. You, your family, or your caregiver should call your doctor right away if you experience any of the following symptoms: panic attacks; agitation or restlessness; new or worsening irritability, anxiety, or depression; acting on dangerous impulses; difficulty falling or staying asleep; aggressive, angry, or violent behavior; mania (frenzied, abnormally excited mood); talking or thinking about wanting to hurt yourself or end your life; withdrawing from friends and family; preoccupation with death and dying; giving away prized possessions; or any other unusual changes in behavior or mood. Be sure that your family or caregiver knows which symptoms may be serious so they can call the doctor if you are unable to seek treatment on your own.
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, continue your normal diet.
What should I do if I forget a dose?
If you forget to take gabapentin capsules, tablets, or oral solution, take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose or if you forget to take gabapentin extended-release tablets, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
What side effects can this medication cause?
Gabapentin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- drowsiness
- tiredness or weakness
- dizziness
- headache
- uncontrollable shaking of a part of your body
- double or blurred vision
- unsteadiness
- anxiety
- memory problems
- strange or unusual thoughts
- unwanted eye movements
- nausea
- vomiting
- heartburn
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- constipation
- increased appetite
- weight gain
- swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- back or joint pain
- fever
- runny nose, sneezing, cough, sore throat, or flu-like symptoms
- ear pain
- red, itchy eyes (sometimes with swelling or discharge)
Some side effects may be serious. If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately:
- rash
- itching
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, or eyes
- hoarseness
- difficulty swallowing or breathing
- seizures
Gabapentin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online (http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch) or by phone (1-800-332-1088).
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store the tablets, extended-release tablets, and capsules at room temperature, away from excess heat and moisture (not in the bathroom). Store the oral solution in the refrigerator.
It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers (such as weekly pill minders and those for eye drops, creams, patches, and inhalers) are not child-resistant and young children can open them easily. To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location – one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach. http://www.upandaway.org
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage/recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your community. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website (http://goo.gl/c4Rm4p) for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
In case of emergency/overdose
In case of overdose, call the poison control helpline at 1-800-222-1222. Information is also available online at https://www.poisonhelp.org/help. If the victim has collapsed, had a seizure, has trouble breathing, or can’t be awakened, immediately call emergency services at 911.
Symptoms of overdose may include the following:
- double vision
- slurred speech
- drowsiness
- diarrhea
What other information should I know?
Keep all appointments with your doctor.
Before having any laboratory test, tell your doctor and the laboratory personnel that you are taking gabapentin.
If you use a dipstick to test your urine for protein, ask your doctor which product you should use while taking this medication.
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
Brand names
- Horizant®
- Neurontin®